Blockchain grants the internet of value to users, taking people’s connectivity one step further.
Over the past 20 years, people partake information through the use of the internet, sending emails to one another, sharing documents, and posting on social media. The blockchain is a reliable technology that connects companies or people on a peer-to-peer or direct basis.
Although blockchain is often stuck up with Bitcoin and other cryptocurrency assets, blockchain also backs decentralized applications (dApps), and complex programming like smart contracts. The efficiency of various transactions and transference of property and rights was undertaken thanks to the smart contracts that blockchain offers.
Blockchain in Easy Terms
Like what its name “blockchain” suggests, it is a chain of blocks that carries information.
A blockchain is a ledger that is entirely accessible to anyone.

In 1991, researchers originally planned to utilize it in timestamping documents. Through blockchain technology, it would be nearly impossible to tamper and backdate documents. After almost two decades, it was left overlooked and neglected until Satoshi Nakamoto, the founder of Bitcoin, utilized it in creating the first cryptocurrency in the market.
The most notable feature of blockchain is its immutability. Once a piece of information is within a blockchain, changing it would be backbreaking.
Blocks
Every block in a blockchain carries the hash of the block, data, and even the hash of the previous block. The data within a block varies depending on the blockchain type. For instance, the Bitcoin blockchain stockpiles records and details of transactions including the amount, who sent it, and who received it.
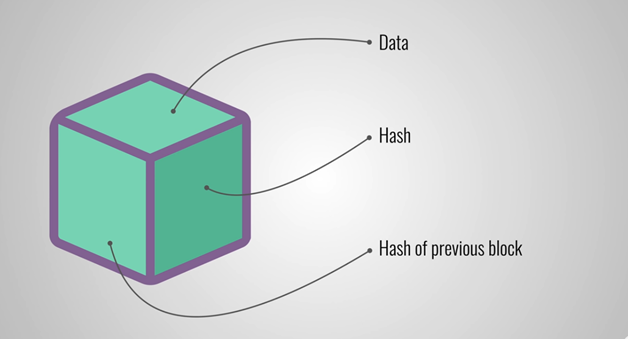
Hash
Others find it complicated to understand what hash is but to put it simply, a hash is something comparable to fingerprints. Like how fingerprints are always unique so they can be used to identify a person, a hash is used in identifying blocks and their entire content.
The hash is being calculated upon the creation of the block, so once even a little change is made within a block, the hash will also change.
To detect changes that happen in a block, the hash is very vital in the blockchain. If there’s a change in the fingerprint of a block, it will no longer be the same block.
Hash of Previous Block
The previous block’s hash stands as one of the elements in a block. Essentially, this is what really creates the chains of blocks, making the blockchain very secure.
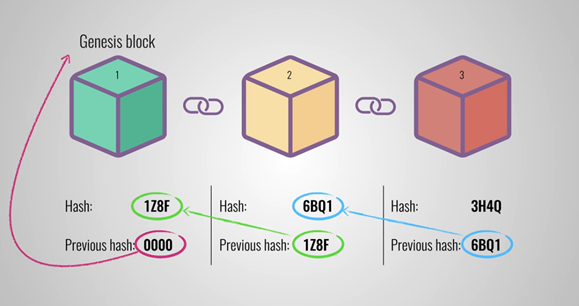
Let’s say you have three blocks in a chain. Every single block contains a hash, as well as the hash of the previous block. Hence, the previous hash of block number three is the hash of block number two, and the previous hash of block number two is the hash of block number one.
The first block in the chain cannot point to a previous hash, simply because it’s the first or starting point of the blockchain. The first block in the chain is referred to as the “genesis block” which means “origin.”
Now, once a person tries tampering with the second block, the hash of the second block will also change. As a consequence, the third and following blocks will deem to be invalid because the records they have in the block are not the same anymore.
The hash is essential for security; however, it is still not enough in preventing tampering.
Nowadays, computers are getting more and more powerful, having the capability to calculate hundreds of thousands of hashes every second. Some are able to tamper blocks, and recalculate every hash of other blocks, making the blockchain valid again.
For tighter blockchain security, blockchains also have proof-of-work (PoW).
Proof of Work
Basically, proof of work is a mechanism intended to slow down the creation of new blocks. In Bitcoin, 10-minutes is allotted to finish necessary proof-of-work before adding a new block to the chain.
Tampering blockchain when there’s proof-of-work is quite difficult because once you tamper with one block, you will need to tamper and recalculate all previous proof-of-work in the following blocks.
Aside from hash and proof-of-work, there is also block distribution which makes blockchains even more secure.
Block Distribution
Rather than having central authorities managing the entire blockchain, blockchain operates through a peer-to-peer (P2P) network, where anyone is free to join.

If a person joins the network, he will acquire the full record of the blockchain, and the node (computers) will be responsible for verifying if everything on the chain is still in place.
Every time a new block is created, the new block is sent to everyone on the network to verify if there’s tampering that occurred in the block. Once the nodes verify that the record is in order, the nodes will add the block to the blockchain.

Before a block gets added to the blockchain, every node should have a consensus, or agreement on which blocks are valid, and which are not. If the nodes cannot verify a block, the network will reject the block and will not add it to the blockchain.
To successfully tamper with the blockchain, a person should tamper with every single block on the chain, revise and tweak the proof-of-work of every block, as well as take control of over 50% of the peer-to-peer network. This is the only way you could tamper with blockchain, a way that is almost impossible to accomplish.
What Lies Ahead Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is persistently advancing, and one of its recent headway is the development of smart contracts. Smart contracts are programs that enable the automatic exchange of coins if a given condition is met.
The world is constantly changing and is heading towards digitalization. If blockchain technology will be implemented in medicine, there will be a more accurate medical record, same goes with e-notary. Even corruption could be minimized if blockchain technology will be used in collecting taxes.
Moreover, blockchain technology and its quick provision of an unchangeable record of the transaction would help in providing shared transaction information across the various location.
It also allows settlement and recording of transactions at the same time while the transaction itself is happening, hence, it helps in gathering real-time data in a recurring formal. This aspect of blockchain technology would help accountancy professionals greatly in the coming years.
What lies ahead of blockchain technology is still uncertain, however, it holds massive potential to create a better world for everyone.



